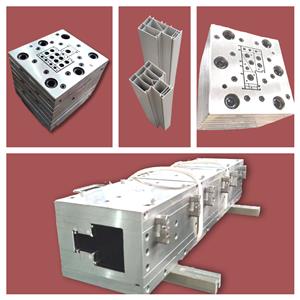
پیویسی پلاسٹک، اخراج مولڈ کی تعمیر، آپ کے لیے پردہ کھولتا ہے۔
عام طور پر استعمال ہونے والے سانچوں کی دو شکلیں ہیں: پلیٹ سٹیپڈ مولڈز اور کراس سیکشنل گریڈینٹ مولڈ۔ پلیٹ سٹیپڈ مولڈ کا بہاؤ کا راستہ قدموں میں بدلتا ہے، جو سلسلہ میں جڑے کئی منہ کے سانچوں سے بنا ہے۔ ہر پلیٹ کو اسی سموچ کی شکل میں مشین بنایا جاتا ہے، جو آہستہ آہستہ انلیٹ کی گول شکل سے مطلوبہ آؤٹ لیٹ شکل میں تبدیل ہو جاتی ہے۔ ایک شکل سے دوسری شکل میں منتقلی کو مکمل کرنے کے لیے ہر بلاک کے ان لیٹ پر بیولز ہوتے ہیں۔ اس قسم کی مولڈ پروسیسنگ لاگت کم ہے، بہاؤ چینل مثالی ہموار نہیں ہے، اور عام طور پر اسے مرکزی پروفائل کے طور پر استعمال کرنے کی ضرورت نہیں ہے۔ سیکشن گریڈیئنٹ مولڈ رنر کو ہموار کیا گیا ہے، رنر میں مواد کا کوئی برقرار رکھنے والا زون نہیں ہو سکتا، پگھلنے کو بتدریج اور درست طریقے سے آؤٹ لیٹ کی شکل کے ہر حصے میں دائرے کے دائرے سے تقسیم کیا جاتا ہے، اور رفتار کو بتدریج بڑھایا جاتا ہے۔ مطلوبہ آؤٹ لیٹ کی رفتار، اور سیکشن پر ہر پوائنٹ کی رفتار ایک جیسی ہے۔ پیچیدہ مولڈ کور والے پیویسی پلاسٹک پروفائلز کے لیے، مولڈ کور یا تو بریکٹ پلیٹ کے ساتھ مربوط ہوتا ہے، کچھ کو بریکٹ پلیٹ میں پنوں اور پیچ کا پتہ لگا کر لگایا جاتا ہے، اور کچھ کو بریکٹ پلیٹ پر سخت جڑنا کے ذریعے سرایت کیا جاتا ہے۔ استعمال کے دوران اسے آسانی سے جدا نہیں کیا جا سکتا، کیونکہ اسے دوبارہ جوڑنے اور ڈیبگ کرنے میں وقت لگتا ہے۔ پگھلنے کا کام بھی دو طریقوں سے کیا جاتا ہے: شنٹ کون پر اور کمپریشن سیکشن میں۔ سیکشن گریڈینٹ مولڈ کو مین پروفائل مولڈ کے طور پر استعمال کیا جا سکتا ہے۔ پی وی سی پلاسٹک پروفائل ایکسٹروژن مولڈ ایکسٹروشن پروڈکشن لائن کا بنیادی حصہ ہے، جس میں ماؤتھ ڈائی (ڈائی ہیڈ بھی کہا جاتا ہے)، شیپنگ مولڈ، کولنگ واٹر ٹینک وغیرہ شامل ہیں۔ ماؤتھ ڈائی کو ایکسٹروڈر ہیڈ پر فلینج کے ساتھ اسمبل کیا جاتا ہے۔ ایک فلینج کا، اور ہیٹنگ رنگ، ہیٹنگ پلیٹ، پاور سپلائی اور تھرموکوپل منسلک ہیں۔ شیپنگ مولڈ اور کولنگ واٹر ٹینک کو شیپنگ ٹیبل پر پیچ کے ساتھ لگایا گیا ہے، اور واٹر پائپ اور گیس پائپ آپس میں جڑے ہوئے ہیں۔ اخراج ڈائی کا بنیادی ڈھانچہ عام طور پر ایک سے زیادہ ٹیمپلیٹ کے اسٹیک اور اسمبل کے ڈھانچے کے طور پر ڈیزائن کیا گیا ہے۔ لہذا، پورے ڈائی کا بہاؤ چینل ٹیمپلیٹ کے ہر ایک ٹکڑے میں، سامنے اور پیچھے کے بہاؤ چینلز میں سے ایک کو جوڑ کر تشکیل دیا جاتا ہے۔ پلیٹ ورک کو پنوں اور بولٹ کے ساتھ کھڑا کیا جاتا ہے اور اسے یک سنگی اخراج ڈائی بنانے کے لیے باندھا جاتا ہے۔ بنیادی صورت حال یہ ہے: ایکسٹروشن ڈائی کا مستقل بہاؤ والا حصہ اکثر سوراخ شدہ پلیٹ اور گردن کے اگلے نصف حصے پر مشتمل ہوتا ہے، اور گردن کے اگلے حصے اور دوسرے حصے کو بھی دو سانچوں کے طور پر ڈیزائن کیا گیا ہے، گردن اور گردن کی منتقلی کی پلیٹ۔ یہ بھی ممکن ہے کہ غیر محفوظ پلیٹ کا استعمال نہ کیا جائے، لیکن بہاؤ کو مستحکم کرنے کے لیے گردن کے بہاؤ چینل کے اگلے نصف حصے کو بیلناکار بہاؤ چینل میں ڈیزائن کیا جائے۔ ایکسٹروشن ڈائی کا اسپلٹ سیکشن گردن کے دوسرے نصف حصے سے شروع ہوتا ہے اور اس میں اسپلٹ کون، اسپلٹ بریکٹ پلیٹ، اور سکڑنے والی پلیٹ شامل ہوتی ہے۔ سکڑنے والی پلیٹ کو ایک فارم ورک میں نہیں بلکہ پہلے سے تیار شدہ پلیٹ کے ساتھ تقسیم کیا جاسکتا ہے - ایک فارم ورک۔ ایکسٹروشن ڈائی کے بنانے والے حصے میں درج ذیل ٹیمپلیٹس شامل ہیں: کیویٹی پلیٹ (جسے پریففارمڈ پلیٹ بھی کہا جاتا ہے)، منہ کا سانچہ (جسے فارمنگ پلیٹ بھی کہا جاتا ہے) اور کور (جسے مولڈ کور بھی کہا جاتا ہے)۔ آسان پروفائل ڈیز کے لیے، پہلے سے تیار شدہ پلیٹ کو منہ کے سانچے کے ساتھ ایک فارم ورک میں ملایا جاتا ہے۔ 1. پروڈکٹ کراس سیکشنل ڈیزائن کے اہم نکات پیویسی پلاسٹک پروفائل پروڈکٹ ڈیزائن کا اہم نکتہ یہ ہے کہ ہر حصے کی موٹائی اور شکل کو ہم آہنگی سے تقسیم کیا جانا چاہئے، تاکہ مشین کے سر میں مواد کا بہاؤ متوازن ہو، کولنگ یکساں ہو سکے۔ ، اور دباؤ متوازن ہوتا ہے۔ عام طور پر، دیوار کی زیادہ سے زیادہ موٹائی اور ایک ہی حصے کی کم از کم دیوار کی موٹائی مختلف ہوتی ہے۔ < 50% is appropriate. If it is a part of a closed rib, the thickness of the rib should be 20% thinner than the wall thickness. In order to avoid the stress concentration at the corner of PVC plastic profile products, the shape change of the product should be smooth and smooth transition, generally the outer corner R is not less than 0.5mm, the inner corner R is not less than 0.25mm. The hollow part of the product should not be too small. The cross-sectional shape is preferably symmetrical. 2. Structure type and design principle of mold The mold is the forming part of the extruder, which is mainly composed of neck seat, shunt cone, support plate (also known as bracket), core mold, mouth template and adjusting screw. PVC plastic profile extrusion die county is mainly composed of three sections: feeding section one by machine base and distribution cone composed of machine head flow channel feeding section, is conical: melt distribution and forming section one by support plate and mouth die compression part constitute melt distribution and forming section, the shape is gradually close to the PVC plastic profile section, parallel section mouth die and core die constitute the machine head parallel section, (1) There are two types of mold structure for extruded plastic profiles: plate head and streamlined head. According to the different methods of processing and manufacturing the machine head, the streamlined head fork is divided into integral streamlined and segmented (also known as stepped) streamlined. (2) Mold design principle The mold is the key part of PVC plastic profile extrusion, and its function is to extrude a blank similar to the profile under the action of 10~25MPa extrusion force. PVC plastic profile mold runner design principle is that the runner section should be streamlined: there is enough compression ratio and shaped length to form a certain extrusion pressure: the flow resistance balance and flow symmetry of the cross-sectional gap of each runner part of the mold. The flow channel structure of the PVC plastic profile head is generally divided into three parts: feeding, compression (also known as transition part) and forming. Generally speaking, the length of the feed part of the long runner is 1 of the length of the shaping part. About 5~2 times, the length of the compression part is about 2~3 times the length of the shaping part. The maximum cross-sectional area of the compression section is in the outlet area of the bracket. The shape of the support ribs of the bracketer. The broad one is jujube nucleus-shaped. The thin ones are long prismatic. The shape of the divergence in the front of the scaffold is that it converges at the same angle on all sides, forming a torpedo body shape. The flow rate of molten material is different in the flow channel of feeding, compression and forming, the feeding part is the smallest, the forming part is the largest, and the transition part must be in between the two and gradually increase in the direction of extrusion. The melt flow rate is inversely proportional to the cross-sectional area of the runner. The roughness of the runner in the head should be Ra0. 4~0.8ym, the roughness of the mouth mold runner of the stereotyped part is higher than the roughness of the inner runner, which should be Ra0.2~0. 4μm, When the extruded billet is just exported to the die, the size of the gap is increased than the mouth die, which is called the mold release expansion, that is, the Balas effect. This effect must be considered when the pulling speed of PVC plastic profile extrusion is slow and it is cooled near the outlet of the die mold. The release mold expansion of the outlet die is usually calculated by volume, and its expansion rate is generally 1.5~2.5 times, and this value changes with different aspects of melt temperature, pressure and velocity. The wall thickness size required for PVC plastic profiles depends on the wall thickness of the appropriate extruded billet on the one hand, and the pulling speed and extrusion amount on the other hand. The thickness of the extrusion blank wall mainly depends on the size of the mouth die gap, and then depends on the plasticizing performance of the material in the extruder, extrusion pressure, extrusion temperature, material performance and expansion value. First, the standard traction shrinkage rate for general wall thickness is ≤2.5%. The gap between the mouth die and the thickness of the product are taken (0.8~0.9) 1 1